
p i,t-1 is the price of security i at the end of the previous trading period (time t-1).The weight of an index for a time period is the total market value of the securities in the index at the end of the previous trading period. I t-1 is the index level at end of the previous period (time t-1) In an index where the individual components are not known, but an index level is available from an external source, such as the Standard & Poor’s 500 Composite Index, the return R t is calculated as follows: This determines whether the index is a total return index or a capital appreciation index. The security returns can be total returns or capital appreciation (returns without dividends). Such an index would consist of n stocks, with the same dollar amount invested in each stock. In an equally-weighted index, the weight is equal and by convention w i,t is set to one for every stock.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/nvda2-475ce0659a0e45a786a6c361a02f0f3d.jpg)
In a value-weighted index, the weight ( w i,t) assigned is its total market value see Index Weight below. (see section xxxx of Stock guide for Security Return Calculation)

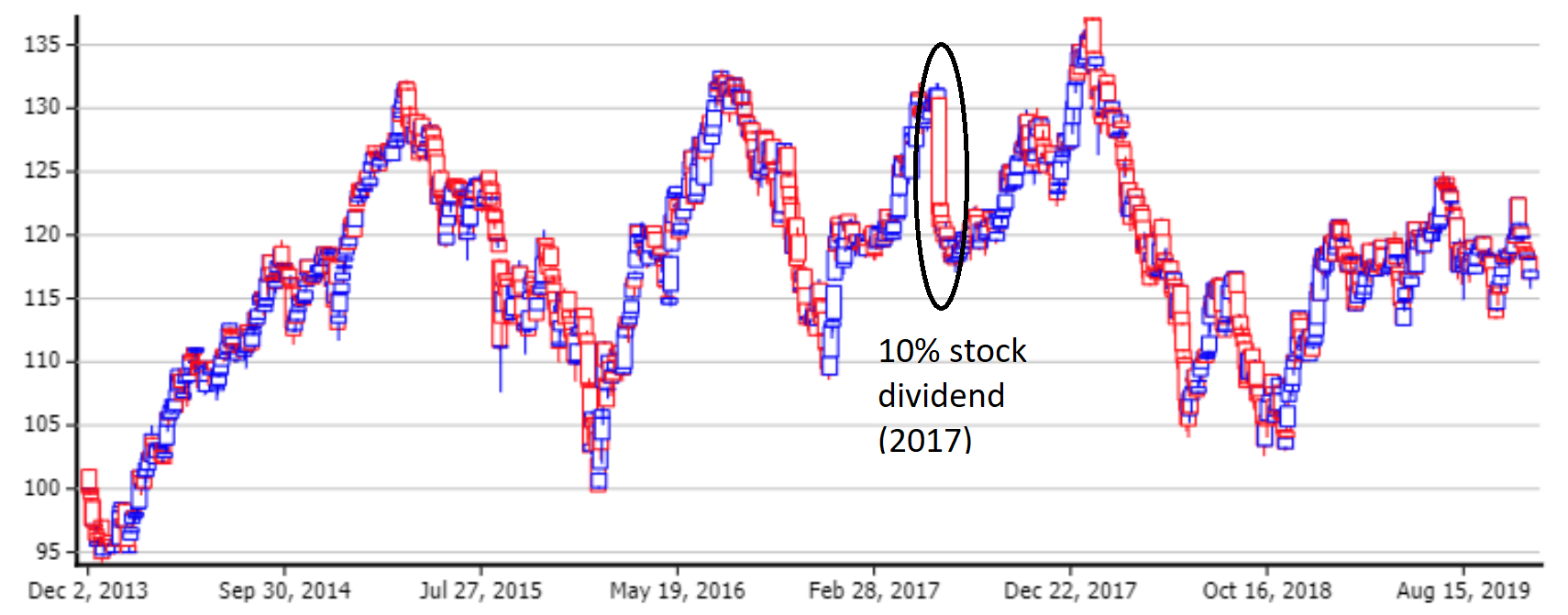
If t-1 < F then I t is set to missing- Note: Missing values are file format specific.ĭefined CRSP indexes use the following initial dates and levels: CRSP Stock File IndexesĬRSP US Government Treasury and Inflation Indexes If t > C 0 and a split event with factor f since t-1 In both cases, where C 0 is the adjustment base date, the cumulative adjustment factor is: Share and volume data are adjusted with the calculation: Where A(t) is the adjusted value at time t, P(t) is the raw value at time t, and C(t) is the cumulative adjustment factor at time t. Price and dividend data are adjusted with the calculation: Split events are applied on the Ex-Distribution Date. Shares and volumes are only adjusted using stock splits and stock dividends. Split events always include stock splits, stock dividends, and other distributions with price factors such as spin-offs, stock distributions, and rights. The adjustment base date is usually chosen to be the last available day of trading. All data on this date are unadjusted, and other data are converted based on the split events between the base date and the time of that data. CRSP provides raw, Unadjusted Data, but data utilities stk_print and ts_print can be used to generate Adjusted Data.Īn adjustment base date is chosen as the anchor date. Price, dividend, shares, and volume data are historically adjusted for split events to make data directly comparable at different times during the history of a security.
This area contains formulas and methodologies used to derive CRSP variables in the stock and index files and generated by the CRSP data utilities.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
